The notions of an entity set and a relationship set are not precise, and it is possible to define a set of entities and the relationships among them in a number of different ways.
Common mistakes in E-R models
- Use of a primary key of an entity set as an attribute of another entity set.
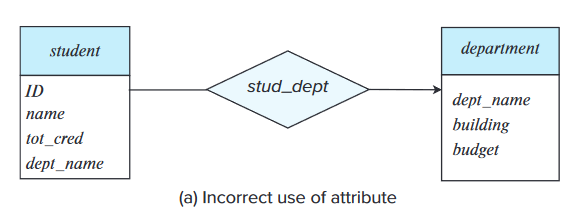
- Use of a relationship with a single-valued attribute in a situation that requires a multivalued attribute.
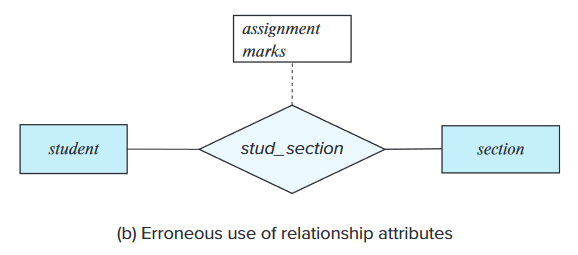
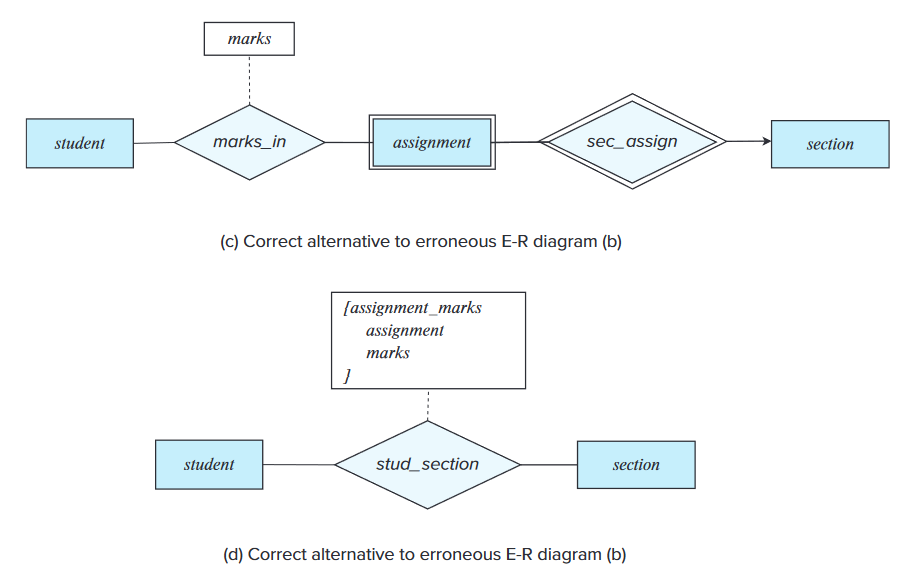
- Possible solutions:
- Use a weak entity set.
- Use a multivalued composite attribute.
Use of entity sets versus attributes
Consider the entity set instructor with the additional attribute phone-number. There are two possible ways to model this as an E-R model:
phone-numberis an attribute of an entityinstructor.phoneis an entity in its own right with attributesphone-number.
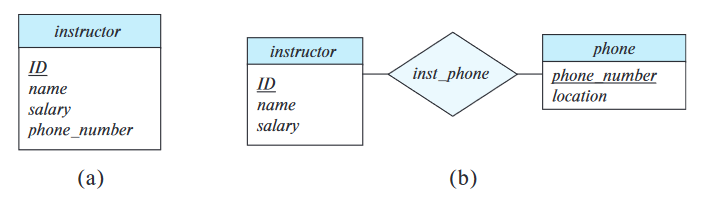
The main difference is that treating a phone as an entity better models a
situation where one may want to keep extra information about a phone, possibly multiple phone-numbers per instructor.
Use of entity sets versus relationship sets
Consider the entity sets section and student, and the relationship between them indicating the section(s) that a student takes. There are two possible ways to model this as an E-R model:
- As a relationship set
takes - As an entity set
registration, and two relationship sets betweenregistrationandsection,student
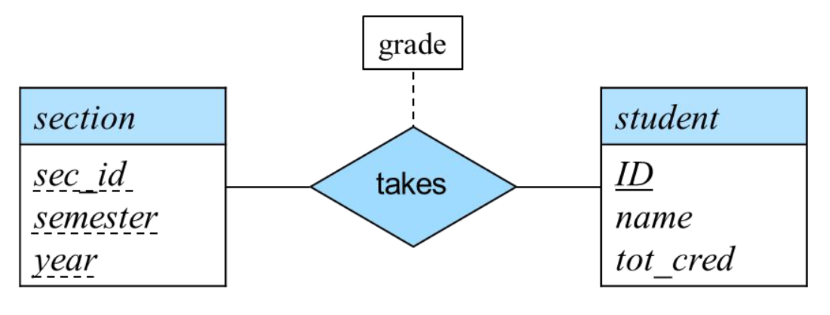
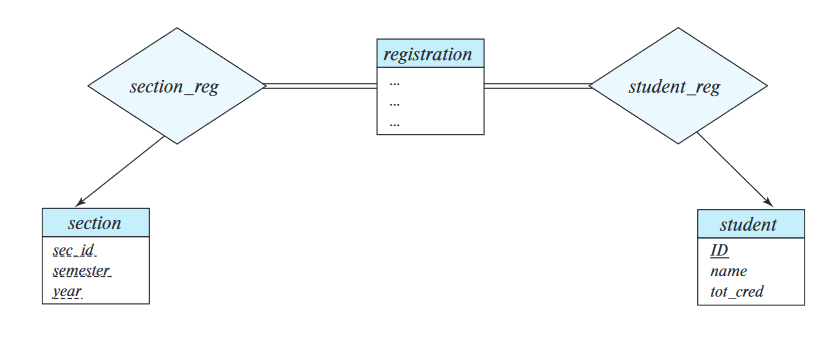
A possible guideline is to designate a relationship set to describe an action that occurs between entities.
Binary versus nonbinary relationships
Although it is possible to replace any nonbinary (-ary, ) relationship set by a number of distinct binary relationship sets, a -ary relationship sets shows more clearly that several entities participate in a single relationship.
However, some relationships that appear to be nonbinary may be better represented using binary relationships.
Converting nonbinary relationships
In general, any nonbinary relationship can be represented using binary relationships by creating an artificial entity set, and creating an identifying attribute for the artificial entity set to other entity sets participating in the relationship.
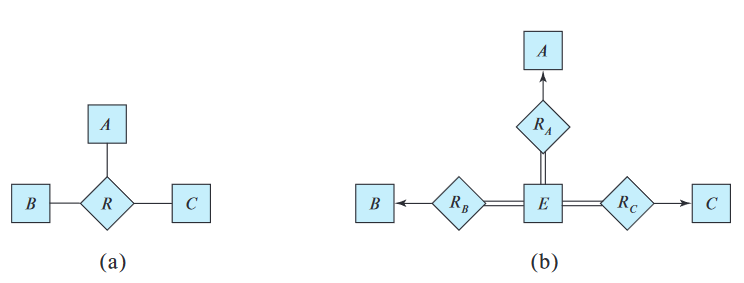
However, this restriction is not always desirable.
- Such restrictions increases the complexity of the design and the overall storage requirements.
- An -ary relationship set shows more clearly that several entities participate in a single relationship.
- Translating all constraints may not be possible.
- There may be instances in the translated schema that cannot correspond to any instance of the original relationship.