A major purpose of a database system is to provide users with an abstract view of the data. That is, the system hides certain details of how the data are stored and maintained.
Data models
A data model is a collection of conceptual tools for describing data, data relationships, data semantics, and consistency constraints.
-
Relational model
All the data is stored in various tables. Each table has multiple columns, and each column has a unique name. Tables are also known as relations.
-
Entity-Relationship model
Uses a collection of basic objects, called entities, and relationships among these objects.
-
Semi-structured data model
-
Object-based data model
Allow procedures to be stored in the database system and executed by the database system.
Data abstraction
The complexity of the data structures to represent data in the database is hidden from users through several levels of data abstraction.
-
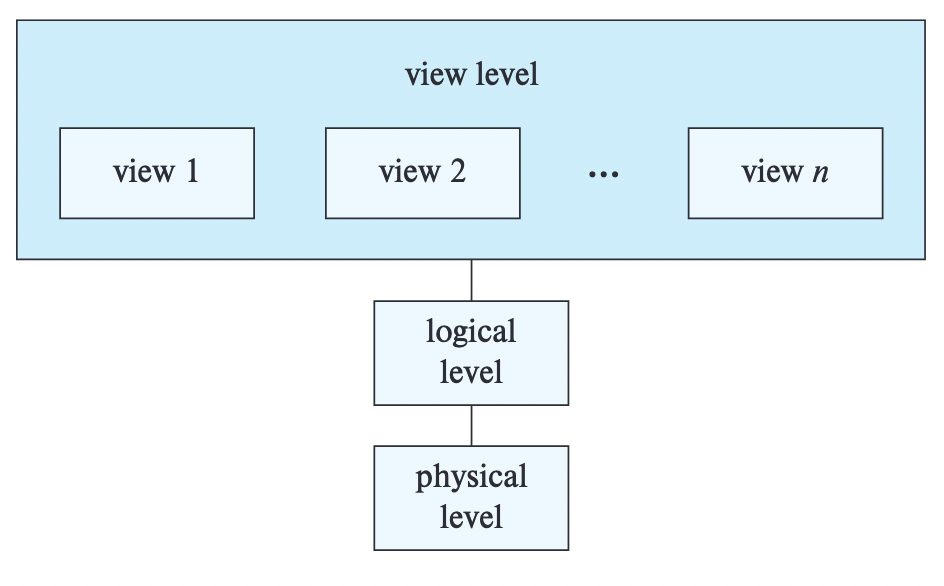
Physical level
Describes how the data are actually stored. It describes complex low-level data structures in detail.
-
Logical level
Describes what data are stored in the database, and what relationships exist among those data.
-
View level
Describes only part of the entire database. The view level of abstraction exists to simplify users’ interaction with the system. The system may provide many views for the same database.
-
Physical data independence
The ability to modify the physical schema without changing the logical schema. In general, the interfaces between the various levels and components should be well defined, so that changes in some parts do not seriously influence others.
Instances and schemas
-
The collection of information stored in the database at a particular moment is called an instance of the database.
-
The overall design of the database is called the database schema. Database systems have several schemas, partitioned according to the levels of abstraction.
-
Physical schema
Describes the overall physical structure of the database.
-
Logical schema
Describes the overall logical structure of the database.
-
Subschema
Describes different views of the database.
-